Whether you’re a small business owner or run a Fortune 500 company, SEO has an enormous impact on the success of your business. Your SEO strategy determines how easily your target customers can find you. Given that 75% of internet users don’t even look past the first page of search results, that’s no easy task.
Here are 12 simple SEO tips and tricks you can use to get your site in front of your future customers:
1. Target Relevant Primary and Secondary Keywords
Keyword research is the foundation of any good SEO strategy. If you know how to use keywords effectively, you can develop content that attracts more people to your website. The first step is to identify your page’s primary and secondary keywords.
Your primary keyword is the main focus of your content. You only need to pick one primary keyword per page. It should be relevant to what your page’s focus, your brand identity, your products, and your services.
Your secondary keywords support the main topic. You will probably have several of these. Often, they’re more granular than the primary keyword and represent subtopics you’re covering throughout an article. Try to include them naturally in your content, but don’t force them if they don’t fit.
You can use the Keyword Magic Tool to find your primary and secondary keywords.

Here’s how it works:
First, enter a seed keyword representing the main topic you want to target.
Next, choose your primary keyword. Try and find one that’s super relevant and aligns with your goals. For example, perhaps you want to write an educational blog post about travel, and you want to find a keyword with a lower difficulty.
Pay close attention to the Questions and Related Keywords sections to build your list of potential supporting keywords.
To learn more, check out our blog post about the four types of keywords you could target.
2. Write Quality Original Content
If you want users to find and return to your site, you need quality content that is original, comprehensive, and evergreen.
Original content shows the audience your unique perspective and expertise and enables them to build a relationship with you. What’s more, search engine algorithms, especially Google, are designed to sniff out unique content. Those who practice good SEO and publish trustworthy original content are likely to increase searches.
Ideally, your content should be comprehensive. That means the content you publish answers everything a user might want to know about that topic. Comprehensive pages help show search engines that you’re an authority on that topic.
The SEO Content Template Tool can help you write more comprehensive content. It analyzes high-ranking competitor content for your target keyword and tells you what attributes you should target to perform well.
Finally, evergreen content has long-term value, which will continue to be relevant and generate traffic over a long period. Inbound marketing is the gift that keeps on giving because it continues to produce results while your focus is elsewhere.
When creating evergreen content, think about what topics will bring long-term value to your readers without needing significant updates. Try to avoid seasonal, breaking news stories, or time-sensitive data stories. These pages are unlikely to remain relevant over time.
3. Format Your Content for Search Engines & Target Featured Snippets
If you want the content you write to perform well, make sure you’re answering the questions your audience is asking. One way to do this is to target featured snippets.
Featured snippets appear at the top of the search results page on Google. They’re designed to answer a user’s question without requiring them to leave the page. They’re highly visible, helpful, and likely to attract organic traffic since they appear before numbered results. You might also see them referred to as SERP features.

These positions are highly sought after by digital marketers. To win one, you need to optimize your content to target them. The strategies you use to target featured snippets can make your content more helpful to readers and improve your SEO, even if you don’t win the snippet in question.
Here’s what to do:
First, choose which content you want to optimize to target a featured snippet. Use the Keyword Magic tool to identify relevant keywords with the search intent and SERP feature you want to target.

Next, search for that keyword yourself to see what type of content is currently featured. Make a note of what question the content answers and how it’s written. You can also see top SERP results in your target location by selecting the triangle next to a keyword in the tool.
For example, is the snippet a bulleted list or a table? Is the information correct? What else ranks well? These observations will give you an idea of how to edit your content.
Now edit your content.
Make sure your content both asks and answers the target question in the snippet as clearly and concisely as possible. After all, studies show that a piece of content that asks a question is more likely to have a featured snippet.
Organize your page using heading and subheaders. If it makes sense for your page, try to use one of your subheaders to target your desired SERP feature. Headings and subheadings make it easy to understand or search your page, which can help improve your search ranking.
Finally, tighten up your page’s copy. Try to use short, direct sentences (no more than 20 words) with language that isn’t too complicated. And while you should try to avoid single-sentence paragraphs, you don’t want them to be too long, either.
4. Optimize Your Page Title and Meta Description
Your page title and meta description might be the first thing your audience ever sees. Users might decide whether to click or skip your page based on these alone. That’s a lot of power for so few words, so make sure they’re impactful.

Typically, whatever platform you use to host your website offers an easy way to edit your page title and meta description. WordPress, for instance, offers two boxes labeled “SEO title” and “meta description.”
Here are a few tips to remember:
- Keep your page title between 30 and 60 characters
- Keep your meta description under 160 characters
- Include your target keyword
- Communicate what your page is about and what makes it unique
- Make sure your title and meta description are unique for every page
5. Use Short, Descriptive URLs
Improving your URL structure can significantly impact your on-page SEO with relatively little effort. A clean URL can help search engines understand your page and gives you a more user-friendly appearance in the SERPs.

Best of all, it’s relatively easy to do, even for SEO beginners.
An effective URL should:
- Use keywords: Try to include your primary keyword, if you can
- Be readable: When your visitor reads the URL, it should be easy for them to understand what the page is about
- Be concise: Shorter URLs (around 60 characters) are preferable. That’s because many search engines can’t process longer URLs and might rank you lower as a result.
6. Generate Backlinks from High Site Authority Websites
Backlinks, or external links leading to your site, are a critical ranking factor. Links from reputable sources can increase your site’s authority and improve your SEO over time. You can acquire those backlinks through a process called link building.
But how do you know which backlink sources to target? It’s simple: find out who your competitors get their backlinks from. Use the Backlink Gap Tool to compare your current backlink profile with your competitors and find new opportunities.

To use the Backlink Gap tool:
- Enter your domain and up to four competitors, and click “Find prospects.”
- Use the report filters to narrow down your results. For example, you might choose to look only at the best opportunities with an Authority Score of 80 or higher.
- Select the backlink opportunities you’re interested in pursuing, and click “Start outreach” to send them to a Link Building tool project. Use the Link Building tool to pursue them without ever leaving Semrush. If you don’t have a current Link Building tool project, you’ll be prompted to create one.
Of course, that’s not the only way to generate backlinks. Here are a few other ideas:
- Offer to write a guest post for other outlets, particularly if you have an interesting infographic or something else to offer.
- Reach out to publishers to cover any original research or data you’ve put together for your on-site content.
- Get listed in industry directories. You may need to join professional industry associations, use local citation services, networking groups, or business organizations, so you can further establish credibility.
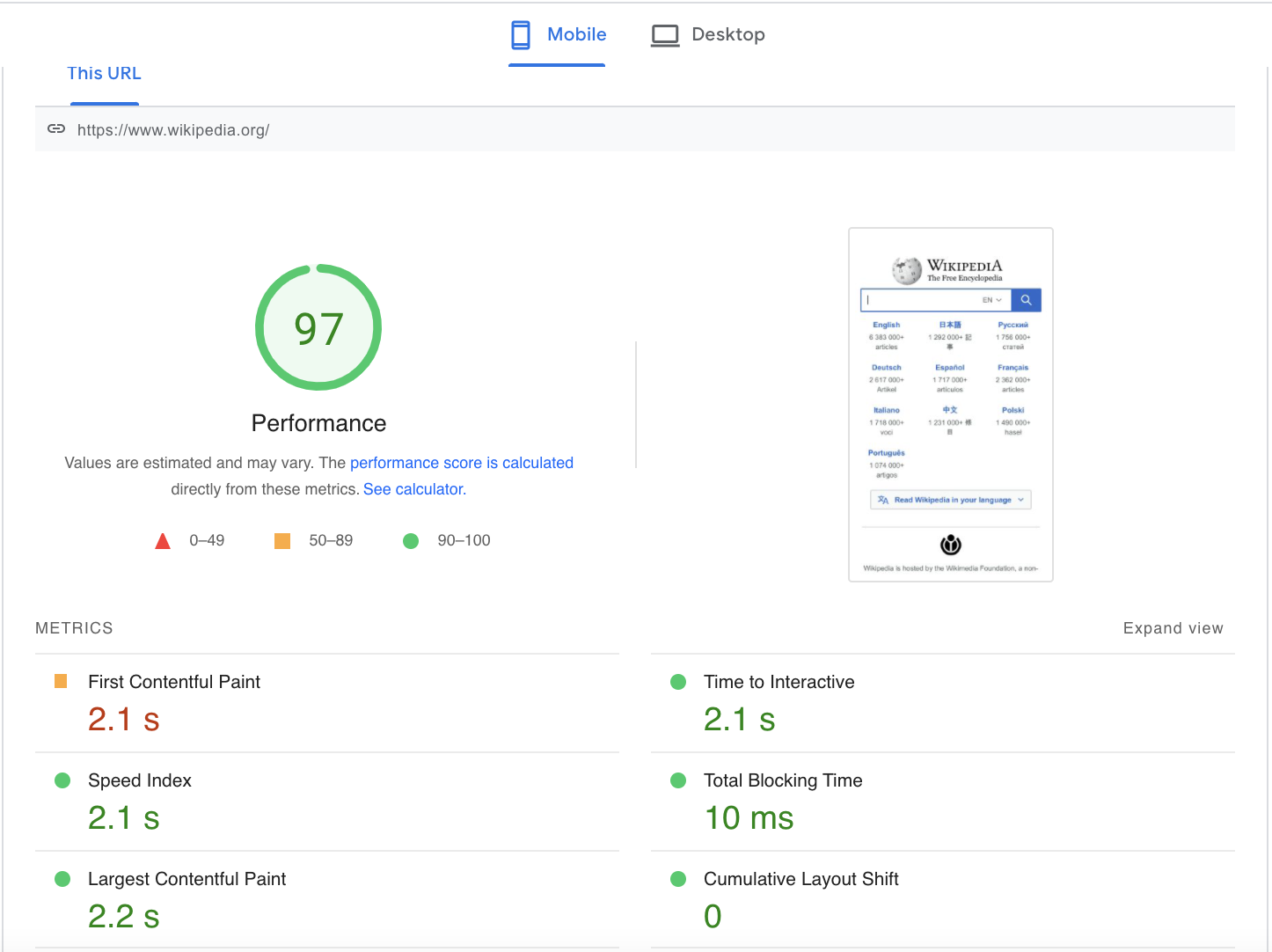
7. Remove Anything That Loads Slowly
Page load time doesn’t just impact user experience. It can also affect your SEO. After all, if a page loads too slowly, users are unlikely to stick around, increasing your bounce rate. A page’s loading time is one of the three Core Web Vitals and a ranking factor.
Google PageSpeed Insights is a free SEO tool that scores your desktop and mobile page speed on a scale of zero to 100, with 100 being the fastest.

If your page loads too slowly, look for page elements that might be increasing your load time. For example, do you have unnecessary plugins added to your page? Try removing them to increase your page’s speed.
You can check your site for this and other factors using the Site Audit tool. Site Audit has over 140 checks for various SEO issues, including slow loading time, HTTPS implementation, markups, Core Web Vitals, broken links, and more. Use it in tandem with PageSpeed insights to ensure your site is up to speed.
8. Use a Mix of Internal and External Links
Using internal and external links effectively can improve crawlability, user experience, and credibility. Ideally, these links should lead to useful, relevant information.
Internal links direct users to other pages on your site. They help search engine crawlers find your content and encourage users to stay on your site longer. For example, you could link between related blog posts to help your audience find more information on a topic they’re researching without ever leaving your site.
External links are links that lead a user to another website. You can use these to link to websites with quality, authoritative content on the topic you’re writing about. Remember to vet your external links before adding them, as linking to low-quality content could negatively impact your credibility.
9. Optimize Your Graphics
It’s hard to resist a colorful graphic or an image that perfectly captures the essence of a topic. If you create such images for your website, make sure they’re optimized. Here are a few things to keep in mind:
- Size and Formatting: Make sure you’re using the image size and file type that works best for your readers. If an image is too large, it could slow down your page. If the file type isn’t supported, the image might not load at all.
- Accessibility: Always include descriptive alt text for each image. Not only does this help make your site more accessible for screen readers, but it also creates opportunities to integrate more supporting keywords. Avoid embedding important text elements in your images unless there’s another way to access them.
- Context: Provide context for your images by placing them beside relevant text on your page. If possible, try to place your most important image near the top of the page.
- Links: Create descriptive names and logical URL structures for all of your images. Not only does this help to optimize them for organic search, but it also makes it easier for others to share your pictures on their sites, potentially granting you backlinks.
- Test: Always remember to test your pages on mobile and desktop. Users tend to search in Google Images from mobile more often than on desktop, so optimizing your images for mobile could have additional benefits.
10. Conduct Regular Site Audits
Performing regular site audits helps to ensure your site remains both functional and user-friendly. It’s also an excellent way to catch issues you might have missed, like broken links, orphaned pages, or slow load times. Then, you can prioritize and address them before they have a significant impact.
To get started:
- Create a new project for your website.
- Specify your page source and how many pages you’d like to crawl.
- Provide any additional specifications, including your crawler settings, disallowed URLs, or URL parameters.
- Run or schedule your site audit.







46 Responses
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/en-IN/register-person?ref=UM6SMJM3
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.info/en/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/bn/register?ref=UM6SMJM3
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.com/si-LK/register-person?ref=V2H9AFPY
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/en-IN/register-person?ref=UM6SMJM3
Terrific work! That is the type of info thuat are supposed too be shared around the web.
Disgrace on Google for now not positioning this publish upper!
Come on over and talk ovger with my web site . Thank you =) https://Glassi-India.mystrikingly.com/
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. binance account
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.info/hu/register-person?ref=IQY5TET4
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.com/pt-BR/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.info/ar/register-person?ref=PORL8W0Z
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/bg/register?ref=V2H9AFPY
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.info/sk/register?ref=WKAGBF7Y
бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом Однако, несмотря на кажущуюся легкость, важно помнить о некоторых нюансах. Даже фриспины без отыгрыша могут иметь ограничения, например, на максимальную сумму вывода или на конкретные слоты, на которых их можно использовать. Также казино может устанавливать минимальную сумму для вывода, что означает, что даже небольшой выигрыш может быть невыведенным, пока не достигнет указанного порога. Всегда внимательно читайте правила и условия акции, чтобы избежать неприятных сюрпризов.
батарея на электропогрузчик вилочный Штабелер Jungheinrich аккумулятор — высокотехнологичные АКБ с емкостью до 600 Ач. Идеальны для складов с высоким трафиком.
Очистка кафеля Москва Реставрация Москва
What’s up to all, how is the whole thing, I think every one is getting more from this web site, and your views are nice for new users.
регистрация leebet casino
como usar un codigo promocional en 1xbet